What we do
Our Expertise

Sustainable Design
The global awareness and drive toward reducing our carbon footprint on the planet has opened the doors to a host of new ‘green’ building materials, products and ideas.
Structural and Civil
Our knowledge and experience in the utilisation of sustainable products include the likes of:
- rammed earth, straw bales, earth bags, gabion retaining walls, natural clay floors, lime plaster and mortar, structural insulated timber panels, dekriet ceilings
- engineered wood/mass timber which includes, cross-laminated timber (CLT), glue-laminated beams (Glulam), laminated veneer lumber (LVL), nail-laminated timber (NLT), dowel-laminated timber (DLT), bamboo.
- recycled materials
- green concrete – making use of various waste materials to greatly reduce the cement content in concrete.
Sustainable ideas and drives include:
- material selection with a focus on those which can be grown in abundance
- construction waste management
- prefabrication
- usage of natural products which are easily sourced with low to zero carbon emission
- attention to material efficiency by volumetric reduction of existing carbon unfriendly products
- using the structural elements as thermal energy banks and for ducting chilled and warm transportation
The future of buildings, their sustainability and their environmental impact is going to change the landscape of the industry as we know it. We are focused on keeping abreast of, and pioneering the use of the latest products, materials and methods.
Mechanical

Water:
- Black water systems
- Grey water systems
- Sewer treatment plants
- Desalination plants, including other filtration and UV applications
- Bore holes
- Rain water harvesting
- Ground water harvesting (ground water sumps typically just pumped out to storm water system)
Hot water heating:
- Instantaneous electrical hot water heating to eliminate standing losses of hot water storage systems
- Detailed energy modelling on hot water circulation systems ensuring smallest pipe sizes and shortest routes (often cast in sleeves) to minimise circulation losses on central hot water system. This is a major oversight in designs as people tend to focus on generating hot water efficiently but then have major losses circulating hot water through a building
- Energy recovery from AC system to heat hot water
- Heat pumps
- Gas heating where piped gas available
- Solar water heating
- Solar PV water heating where we eliminate circulating hot water through pipes to a roof but rather use PV. PV is less efficient than solar water but once you consider the losses in circulating hot water and the cost of solar water vs solar PV panels this is a very good alternative missed by most
XA Modelling:
- SANS 10400 XA Rational assessments
HVAC technologies:
- TABS
- Ammonia chillers
- Geothermal
- Economy cycle HVAC systems. When it is cool outside dampers open and the air supplied is the cool outside air rather than having to cool down the warmer air inside the building. Free cooling
- Energy recovery AC systems to generate hot water with waste heat
- Energy recovery wheel or Enthalpy wheel. Where air exhausted from an airconditioned space energy is recovered and transferred to the fresh air being pumped back into the space
- Ice storage to generate coolth at night at cheaper electricity rates and use during the day to reduce your peak demand. This reduces the peak demand and electrical infrastructure.

Electrical and Electronic
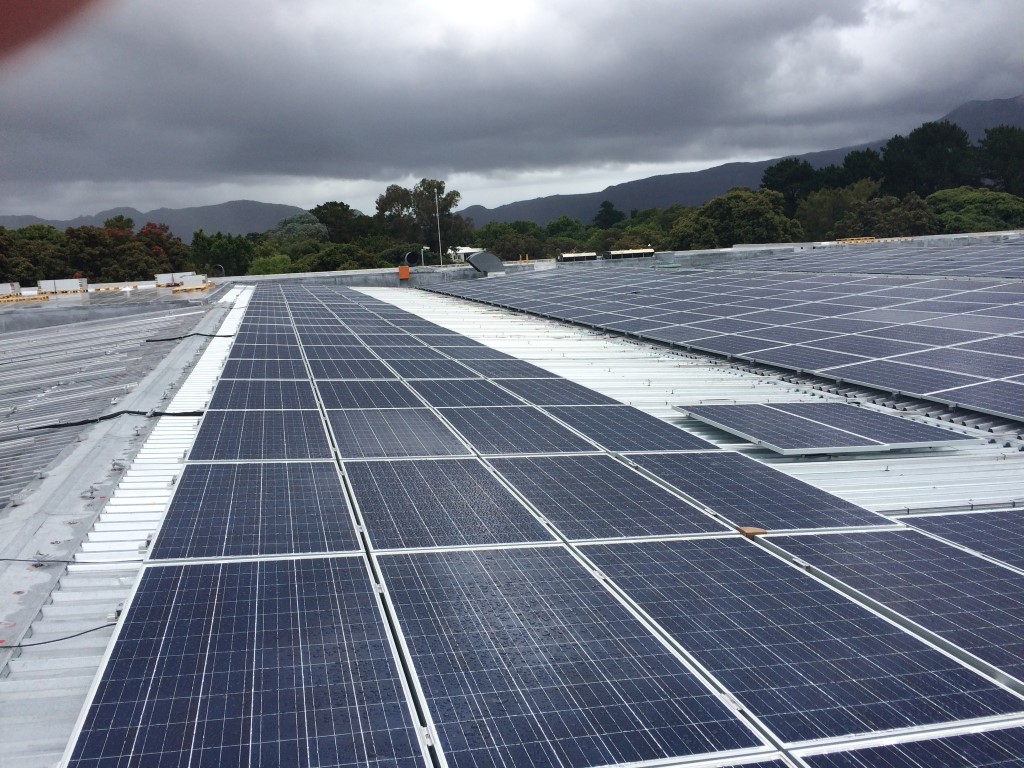

- Rooftop solar PV systems grid tied to the council electrical network to the reduce CO2 emissions and the monthly cost of electricity.
- Islanded rooftop solar PV systems with Lithium batteries for reduced reliance on the electrical grid.
- BMS systems to effectively and efficiently run and monitor the MEP system within the building.
- Lighting control systems to optimise lighting energy use.
- Specification of the latest generation LED lighting to reduce energy consumption.
- Optimisation of the electrical infrastructure and reticulation to lower energy losses and running costs.
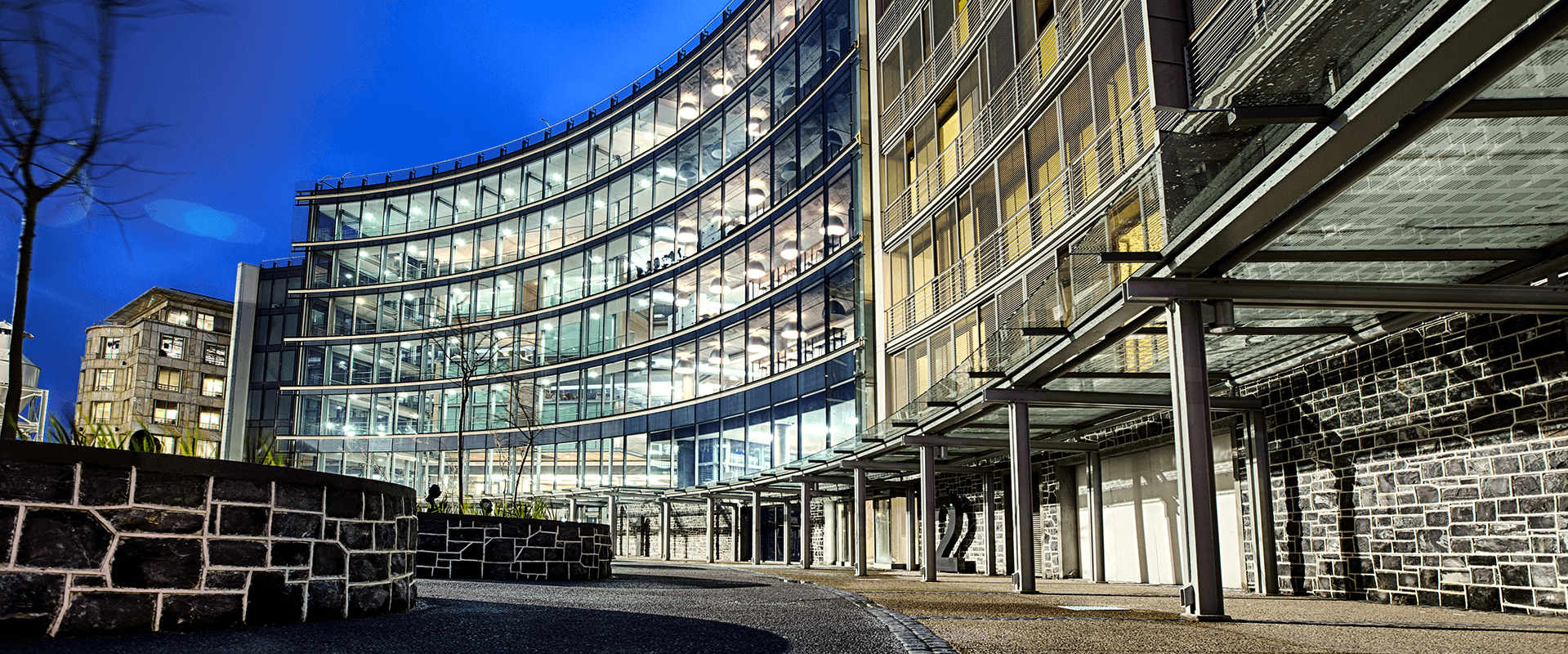
No 1 Silo Square
18,000m² development. 800 new basement parking bays below sea level. Corporate Head Office, 30 Residential Apartments and Various Retail Outlets.
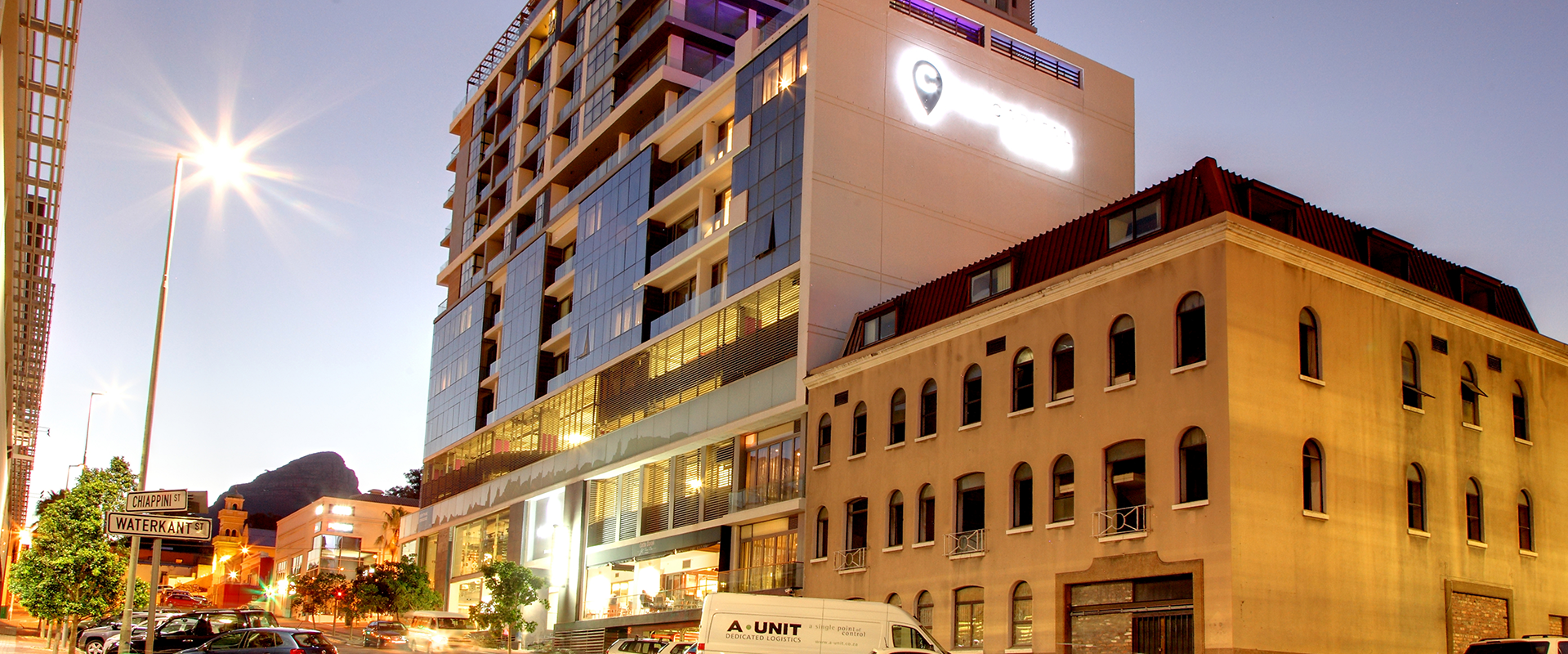

The Mirage
Twenty One storey mixed use development comprising four underground parking decks with seventeen levels above ground, serviced by six 1,000kg elevators.
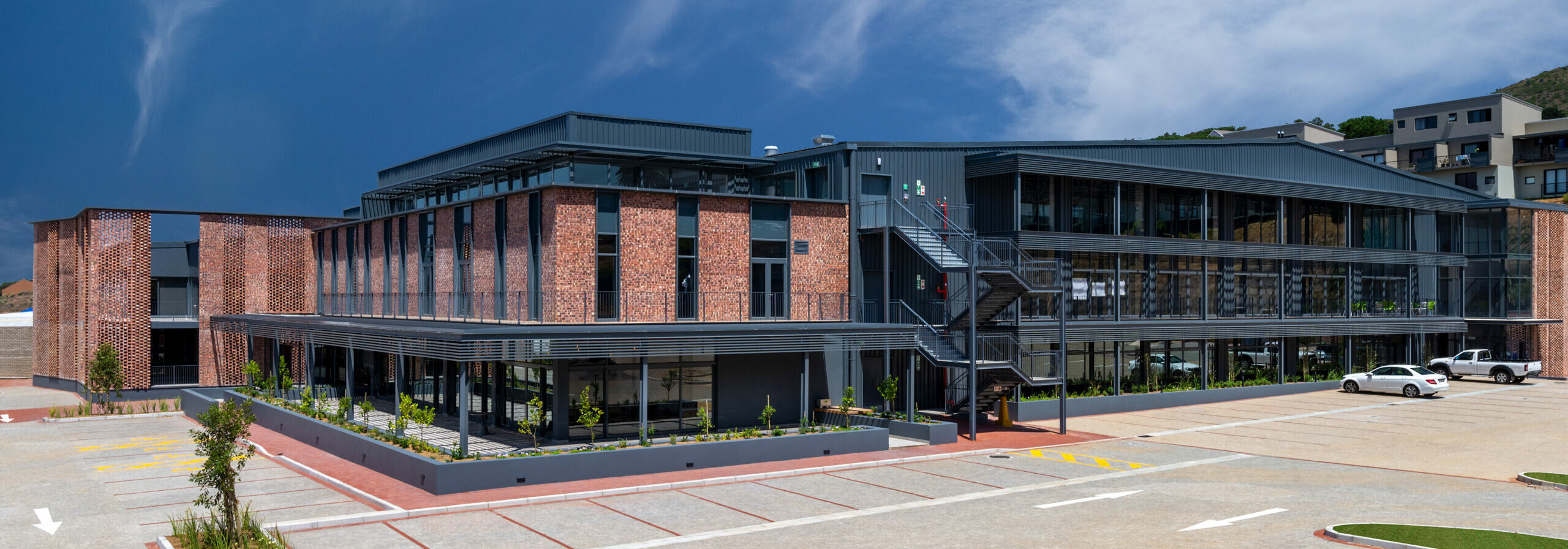

Brickfield Canvas
Refurbishment of a 3,500m² open warehouse space into an exciting 10,400m² A-Grade Commercial Office.